Operate Guide
Complete guide for using AI-powered Kubernetes operations through MCP (Model Context Protocol).
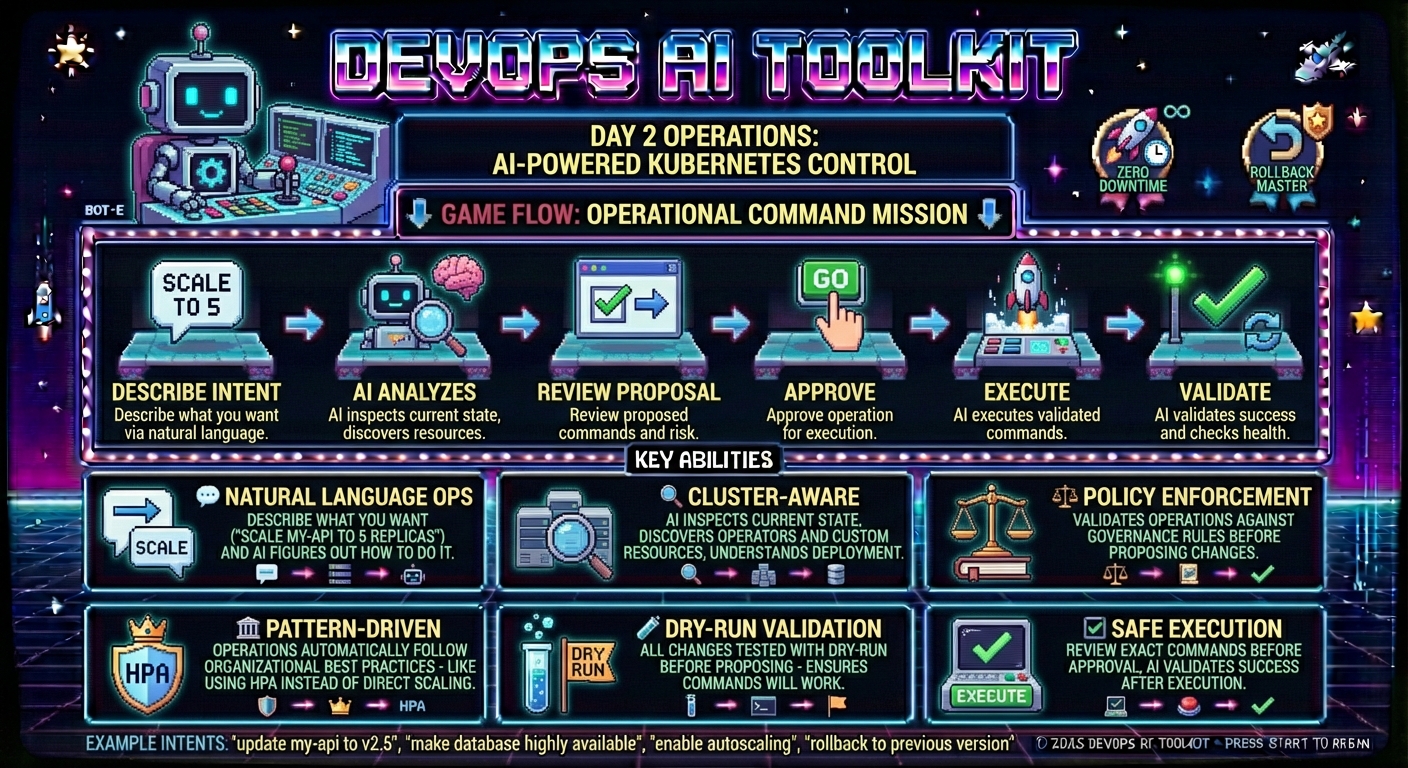
Using via Web UI
These tools are also available through the Web Dashboard.
Prerequisites
Before using this guide, complete the MCP Setup to configure your MCP server with:
- DevOps AI Toolkit MCP server running
- AI model API key configured (see AI Model Configuration for supported models and setup)
KUBECONFIGpointing to your Kubernetes cluster
Required - Capability Management:
- Vector DB service (Qdrant) for capability storage
- Cluster capabilities discovered via Capability Management Guide
- Note: Operations will fail without capabilities - the system requires semantic understanding of your cluster resources
Optional - Enhanced with Organizational Context:
- Organizational patterns created via Pattern Management Guide
- Policy intents created via Policy Management Guide
- When configured, operations automatically follow organizational best practices and governance rules
Overview
What it does: Provides AI-powered Day 2 operations for any Kubernetes resources through natural language intents. Updates, scales, enhances, and manages workloads, databases, infrastructure, and cloud resources with cluster-aware recommendations and organizational governance.
Use when: You need to perform operational changes on deployed resources - applications, databases, storage, AWS/Azure/GCP resources via operators, networking, or any Kubernetes-managed infrastructure.
📖 Full Guide: This document covers the complete operations workflow with detailed examples and behind-the-scenes explanations.
Key Features
The DevOps AI Toolkit operate feature provides:
- Natural language operations - Describe what you want, AI figures out how to do it
- Cluster-aware decisions - Leverages installed operators and custom resources automatically
- Pattern-driven operations - Applies organizational best practices to every change
- Policy enforcement - Validates operations against governance rules before execution
- Dry-run validation - All changes tested before proposing to ensure they'll work
- Safe execution - Exact approved commands executed with comprehensive validation
- Iterative validation - Verifies operations completed successfully with AI analysis
How AI-Driven Operations Work
Traditional Problem: Manual operations require deep Kubernetes expertise, error-prone YAML editing, and knowing which operators/resources are available.
AI Operations Solution: Natural language intents analyzed by AI with full cluster awareness and organizational context.
Operations Flow:
- Intent Analysis: AI understands your operational goal
- Cluster Investigation: AI inspects current state and discovers relevant resources
- Context Integration: Applies relevant organizational patterns, policies, and cluster capabilities
- Solution Design: Generates operational plan that satisfies your intent
- Dry-Run Validation: Tests all changes to ensure they'll succeed
- User Approval: Review proposed changes with full transparency
- Execution: Approved commands executed exactly as shown
- Validation: AI verifies operation completed successfully
Complete Workflow Example
Pattern-Driven Scaling with HPA Creation
This example demonstrates how organizational patterns influence operational decisions. We'll scale a deployment twice:
- Without pattern - AI recommends direct replica scaling
- With pattern - Same intent, but AI creates HPA instead
Scenario Setup:
# Deployment exists: demo-api in operate-demo namespace
# Current state: 2 replicas, nginx:1.21, with resource requests/limits
Step 1: Baseline Operation (No Pattern)
First, let's see what AI recommends without any organizational patterns:
User: scale demo-api deployment in operate-demo namespace to 4 replicas
Agent: Let me analyze the current state and propose a scaling operation.
[Uses mcp__dot-ai__operate with intent "scale demo-api deployment in operate-demo namespace to 4 replicas"]
**Analysis Complete:**
Scaling demo-api deployment from 2 to 4 replicas in the operate-demo namespace. This is a simple, low-risk scaling operation that will increase application availability and capacity.
**Current State:**
- Deployment: demo-api (operate-demo namespace)
- Current replicas: 2/2 running
- Image: nginx:1.21
- Strategy: RollingUpdate (25% max unavailable/surge)
- Resources: 100m CPU/128Mi memory requests, 200m CPU/256Mi memory limits
**Proposed Changes:**
- **Update Deployment** demo-api: replicas: 4 (increased from 2)
- Rationale: Directly satisfies the operational intent to scale deployment to 4 replicas
**Commands to Execute:**
```bash
kubectl scale deployment demo-api --replicas=4 -n operate-demo
```
**✅ Dry-Run Validation:** Success - Deployment accepts the replica count modification
**Patterns Applied:** None
**Capabilities Used:** Deployment
**Policies Checked:**
- Applications must NEVER use 'latest' tag - PASSED (uses nginx:1.21)
**Risk Assessment:** LOW RISK
- Scaling operation is non-disruptive
- New pods created in parallel with existing configuration
- No downtime expected, easily reversible
**Session ID:** opr-1763169767759-0c2a4bb7
📊 **Visualization:** http://localhost:3000/v/opr-1763169767759-0c2a4bb7
Would you like to execute this operation?
Visualization (Optional)
The visualization URL opens an interactive analysis view in the Web UI:
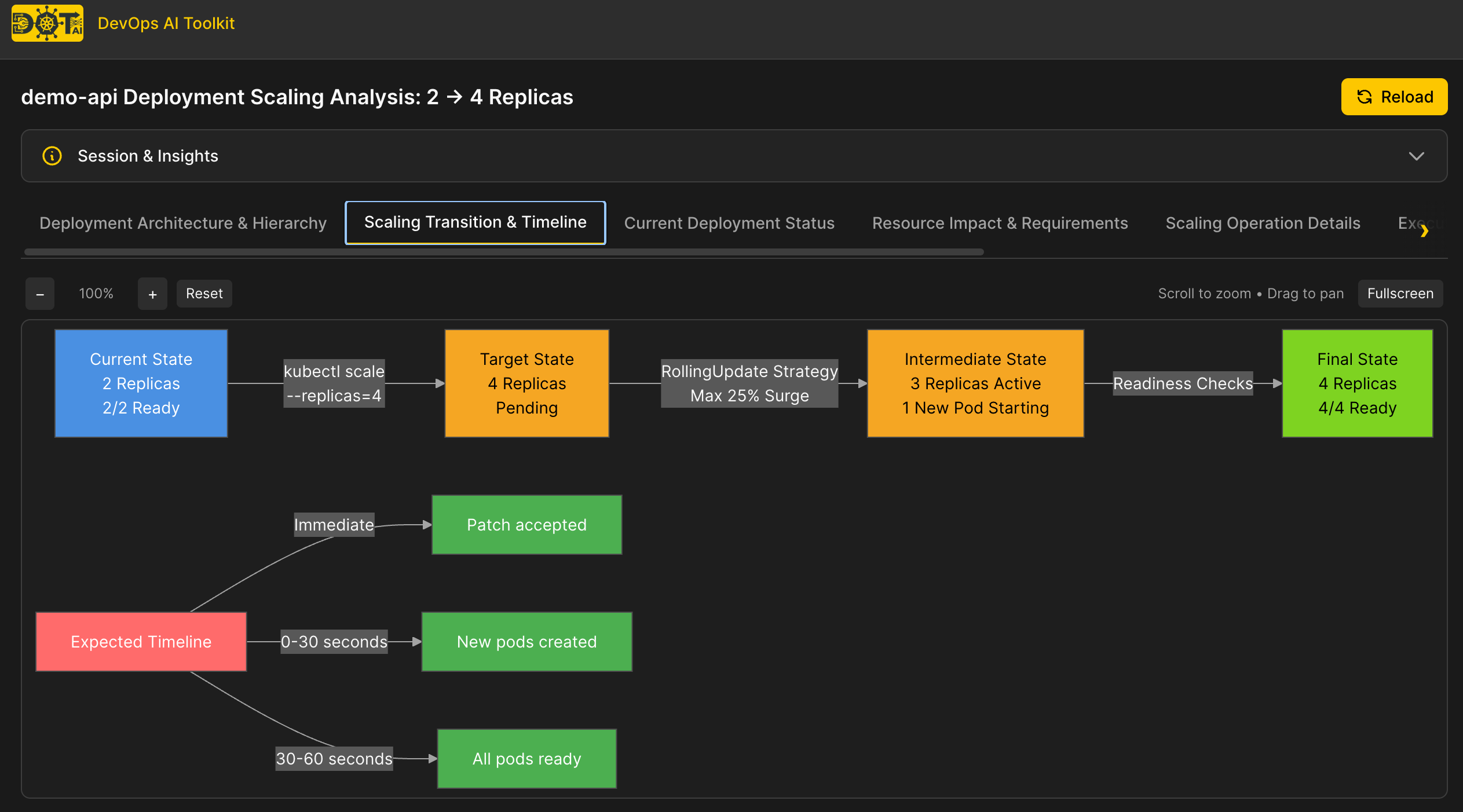
Note: Visualization URLs require additional setup:
- Configure
webUI.baseUrlin your Helm values (see MCP Setup - Web UI Visualization)- Install the Web UI (see Web UI Documentation)
What happened behind the scenes:
- AI analyzed deployment and discovered current state: 2 replicas, properly configured resources
- No organizational patterns found related to "scaling"
- Generated simple
kubectl scalecommand - direct approach - Validated with dry-run successfully
- Proposed straightforward replica increase
Note: Without patterns, AI takes the most direct approach - modifying replicas directly. This works, but doesn't capture organizational best practices like using HPA for managed scaling.
Step 2: Create Organizational Pattern
Now let's create a pattern to enforce organizational best practice - using HPA for scaling operations:
User: I want to create a pattern for horizontal scaling using HPA
Agent: I'll help you create an organizational pattern. Let me start the workflow.
[Uses mcp__dot-ai__manageOrgData with dataType: "pattern", operation: "create"]
**Pattern Creation Workflow** (7 steps):
1. **Description:** "Horizontal scaling with HPA"
2. **Initial triggers:** "applications, scaling, replicas, horizontal"
3. **Expanded triggers:** "HorizontalPodAutoscaler, scaling, horizontal scaling"
4. **Suggested resources:** "HorizontalPodAutoscaler"
5. **Rationale:** "All scaling operations should use HorizontalPodAutoscaler for managing multiple replicas, even if both min and max are the same."
6. **Created by:** "documentation-team"
7. **Review & confirm:** ✅
**Pattern Created Successfully!**
- Pattern ID: 179c61a6-3662-44ba-879f-dfb0fb15d4d2
- Stored in vector database
- Ready to enhance AI recommendations
What happened behind the scenes:
- Pattern workflow gathered all necessary metadata
- Pattern stored in Qdrant vector database with semantic embeddings
- AI can now find this pattern via semantic search when users request scaling operations
- Pattern will influence operational recommendations automatically
Step 3: Pattern-Influenced Operation
Now let's run the exact same scaling intent and see how the pattern changes the recommendation:
User: scale demo-api deployment in operate-demo namespace to 4 replicas. Start the process again.
Agent: Let me analyze the operation with organizational patterns applied.
[Uses mcp__dot-ai__operate with intent "scale demo-api deployment in operate-demo namespace to 4 replicas"]
**Analysis Complete:**
Scaling demo-api deployment from 2 to 4 replicas using HorizontalPodAutoscaler as per organizational Pattern 1 (Horizontal scaling with HPA). The pattern specifies that all scaling operations should use HPA for managing multiple replicas, even when both min and max are set to the same value.
**Current State:**
- Deployment: demo-api (operate-demo namespace)
- Current replicas: 2 running
- Image: nginx:1.21
- Resource requests: 100m CPU / 128Mi memory (HPA-ready)
- No HPA configured
**Proposed Changes:**
- **Create HorizontalPodAutoscaler** demo-api
- minReplicas: 4, maxReplicas: 4
- CPU utilization target: 80%
- Rationale: Follows organizational Pattern 1 which requires all scaling operations to use HPA for consistency and operational best practices. Creates foundation for future autoscaling enhancements.
**HPA Manifest:**
```yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: demo-api
namespace: operate-demo
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: demo-api
minReplicas: 4
maxReplicas: 4
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 80
```
**✅ Dry-Run Validation:** Success - Cluster accepted the HPA resource definition
**Patterns Applied:**
- Pattern 1: Horizontal scaling with HPA - All scaling operations use HorizontalPodAutoscaler for consistency and operational governance
**Capabilities Used:** HorizontalPodAutoscaler (autoscaling/v2)
**Risk Assessment:** LOW RISK
- Scaling up from 2 to 4 replicas on healthy deployment
- Existing pods continue running while new replicas created
- Easily reversible by deleting HPA or adjusting counts
**Session ID:** opr-1763170292295-0dbae152
Would you like to execute this operation?
What happened behind the scenes:
- Vector search found relevant pattern: "Horizontal scaling with HPA" (semantic match on "scaling", "replicas")
- AI read pattern rationale: "All scaling operations should use HorizontalPodAutoscaler..."
- AI changed strategy from direct replica scaling to HPA creation
- Generated HPA manifest with minReplicas=maxReplicas=4 to lock at desired count
- Validated HPA manifest with dry-run successfully
- Listed pattern in "patternsApplied" field for audit trail
Key Difference: Same intent, completely different approach! Pattern transformed a simple kubectl scale into an HPA resource, enforcing organizational best practice.
Step 4: Execute and Validate
Let's approve the operation and watch it execute:
User: Yes, execute the operation
Agent: Executing approved operation and validating results.
[Uses mcp__dot-ai__operate with sessionId: "opr-1763170292295-0dbae152", executeChoice: 1]
**Execution Results:**
✅ **Command 1:** HPA creation
```bash
kubectl apply -f - <<'EOF'
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
...
EOF
```
**Output:** `horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/demo-api created`
**Status:** Success
**AI Validation (Confidence: 98%):**
HPA successfully created and reconciled. The controller scaled the deployment from 2 to 4 replicas as specified by MinReplicas=4/MaxReplicas=4 configuration.
**Verification Results:**
- ✅ 4 pods running in operate-demo namespace
- ✅ All pods in Running state
- ✅ HPA status: 4 current / 4 desired replicas
- ✅ Deployment scaled successfully from 2 to 4 replicas
**Operation completed successfully!**
What happened behind the scenes:
- MCP server executed the approved kubectl command exactly as shown
- HPA resource created in cluster
- HPA controller detected new HPA and reconciled deployment
- Deployment scaled from 2 to 4 replicas automatically
- AI used remediate tool internally to validate success
- AI confirmed all 4 pods running and HPA operational
- Complete audit trail maintained in session
Summary
This example demonstrated:
- Baseline behavior - Without patterns, AI recommends direct approach (kubectl scale)
- Pattern creation - Define organizational best practice (use HPA for scaling)
- Pattern influence - Same intent produces different recommendation (HPA creation)
- Safe execution - Exact approved commands executed with AI validation
Key Takeaway: Organizational patterns transform operations from "what works" to "what's best for your organization" - automatically enforcing governance without manual intervention.
Learn More:
- See Pattern Management Guide for detailed information on creating and managing organizational patterns
- Explore Policy Management Guide for governance and compliance enforcement
Operational Flexibility
The operate tool is fully general-purpose - it handles any Kubernetes operational change through natural language intents:
# The tool figures out how to accomplish your goal
operate(intent="update my-api to version v2.5.0")
operate(intent="make my-database highly available with backups")
operate(intent="enable autoscaling for my-api based on CPU")
operate(intent="rollback my-api to previous version")
operate(intent="add Prometheus monitoring to my-api")
How it works: AI analyzes your intent, inspects cluster state, applies organizational patterns/policies, generates appropriate Kubernetes resources (create/update/delete), validates with dry-run, and proposes exact commands for your approval.
Best Practices
Writing Effective Intents
Be specific about target resources:
✅ Good: "scale demo-api deployment in production namespace to 5 replicas"
❌ Vague: "scale the app"
Include namespace when working with multiple environments:
✅ Good: "update my-api in staging namespace to v2.0"
❌ Ambiguous: "update my-api to v2.0" (which namespace?)
Specify operational requirements when relevant:
✅ Good: "update my-api to v2.0 with zero downtime"
✅ Good: "make my-database highly available with backups"
Session Management
- Review proposals carefully - Always review proposed changes before execution
- Sessions are temporary - Session data expires after operation completion
- Refine if needed - Use
refinedIntentparameter to clarify ambiguous requests
Pattern and Policy Integration
- Create patterns proactively - Define operational best practices before they're needed
- Use specific triggers - Patterns with clear triggers match more accurately
- Document rationale - Clear rationale helps AI apply patterns correctly
- Test patterns - Verify patterns influence recommendations as expected
Troubleshooting
Operation Fails with "No capabilities found"
Problem: Operate tool requires cluster capabilities for semantic resource matching.
Solution: Use the controller for automatic capability scanning (recommended), or scan manually if the controller cannot reach MCP:
# Manual scan (only if controller not available)
User: Scan my cluster capabilities
[Uses mcp__dot-ai__manageOrgData with dataType: "capabilities", operation: "scan"]
See Capability Management Guide for controller setup and manual scanning options.
Pattern Not Applied to Operation
Problem: Created a pattern but operate tool doesn't use it.
Possible causes:
- Trigger mismatch - Pattern triggers don't match your operational intent keywords
- Vector search ranking - Other patterns ranked higher for your intent
- Pattern not stored - Pattern creation didn't complete successfully
Solution:
- Review pattern triggers and ensure they match your intent keywords
- Check pattern was stored:
manageOrgData({ dataType: "pattern", operation: "list" }) - Try more specific intent wording that matches pattern triggers
Dry-Run Validation Fails
Problem: AI reports dry-run validation failures.
This is expected behavior - AI iterates to fix validation errors:
- AI generates manifest
- Dry-run validates and reports errors
- AI fixes errors based on feedback
- Retries validation (up to 30 iterations)
If validation still fails after iterations, AI will report the specific issue for manual review.
Related Guides
- MCP Recommendation Guide - Initial application deployment with capability-enhanced recommendations
- MCP Remediate Guide - AI-powered troubleshooting and issue resolution
- Pattern Management Guide - Creating and managing organizational patterns
- Policy Management Guide - Defining and enforcing governance policies
- Capability Management Guide - Cluster resource discovery and semantic capabilities